The hidden internet has long been wrapped in mystery, often described as a shadowy underworld crammed with illicit activities and concealed agendas. Yet, beneath this fascinating surface lies a intricate environment of online marketplaces that serve a variety of needs and demands. Comprehending these dark web markets requires delving into a realm that operates beyond the traditional internet, where secrecy is cherished and exchanges can vary from the illicit to the harmless.
As users explore the darknet, they meet a diverse selection of platforms, each with its own traits and offerings. From forbidden goods and services to safe communications and privacy-oriented products, the dark web provides a varied environment that questions our understandings of digital engagement. In this article, we will explore the existing state of dark web markets, investigating their framework, the character of their exchanges, and the socio-economic factors that contribute to their presence. By shedding light on this concealed realm, we aim to provide a clearer insight of what motivates these markets and the consequences they hold for society at a general level.
An Overview of this Dark Web
The dark web is a minor part of the internet that is deliberately hidden and inaccessible through common web browsers. It requires specialized software, configurations, or authorization to access, the most prevalent being Tor, which permits users to browse without revealing their identity. In contrast to the surface web, the dark web is commonly linked to illegal activities, but it also serves lawful purposes, such as offering a platform for free speech in oppressive regimes and safeguarding privacy.
Navigating the dark web can be daunting due to its special structure. Content is arranged into numerous markets, forums, and websites, each catering to various interests and communities. The markets on this layer of the web operate in a manner akin to traditional e-commerce platforms but generally focus on the sale of illegal goods and services, including drugs, weapons, and stolen data. However, users should be cautious, as these spaces can also house scams and harmful individuals.
The technologies that preserve the dark web's anonymity reach past against government surveillance or censorship. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are frequently utilized for transactions to ensure that the identities of buyers and sellers remain obscured. This financial layer adds an intricate dimension to the marketplace dynamics, where trust is commonly developed through user ratings and feedback systems, akin to those found in more familiar digital marketplaces.
Key Players in the Anonymous Market
The underground market landscape is populated by a diversity of actors, all playing a specific role in its intricate ecosystem. At the forefront are the market operators, who create and maintain the venues where goods and services are purchased and sold. These individuals are often extremely experienced in technology, using sophisticated coding and security measures to protect their sites from law enforcement agencies and competing markets. Their capability to adapt to changes in the digital landscape is vital for the market's sustainability and user trust.
Another important group comprises the sellers, who supply an range of products including illegal drugs and weapons to counterfeit goods and hacking services. These vendors establish their credibility through user ratings and feedback, which can greatly impact their revenue. Many use nicknames to conceal their identities while leveraging various marketing approaches to promote their products. The competitive dynamic of the darknet market drives these vendors to innovate, constantly finding new methods to attract buyers and keep a consistent customer base.
Finally, the customers themselves form the backbone of the darknet market. Buyers are drawn to these platforms for their perceived privacy, accessing items that may be hard or infeasible to obtain through conventional means. They are often well-versed in cybersecurity practices, using tools like encrypted communication and cryptocurrencies to safeguard their exchanges. The interaction between users and vendors creates a dynamic environment where trust and reputation are paramount, shaping the overall health and activity level of the darknet markets .
Threats and Legal Consequences
Participating with darkweb markets presents significant risks that can have severe consequences for participants. One of the primary concerns is the potential for facing scams or fraudulent listings. Many vendors exploit the anonymity of the dark web to create sites that seem legitimate but fade away with users' funds. Buyers may receive fake products or no product at all, resulting in financial loss and frustration.
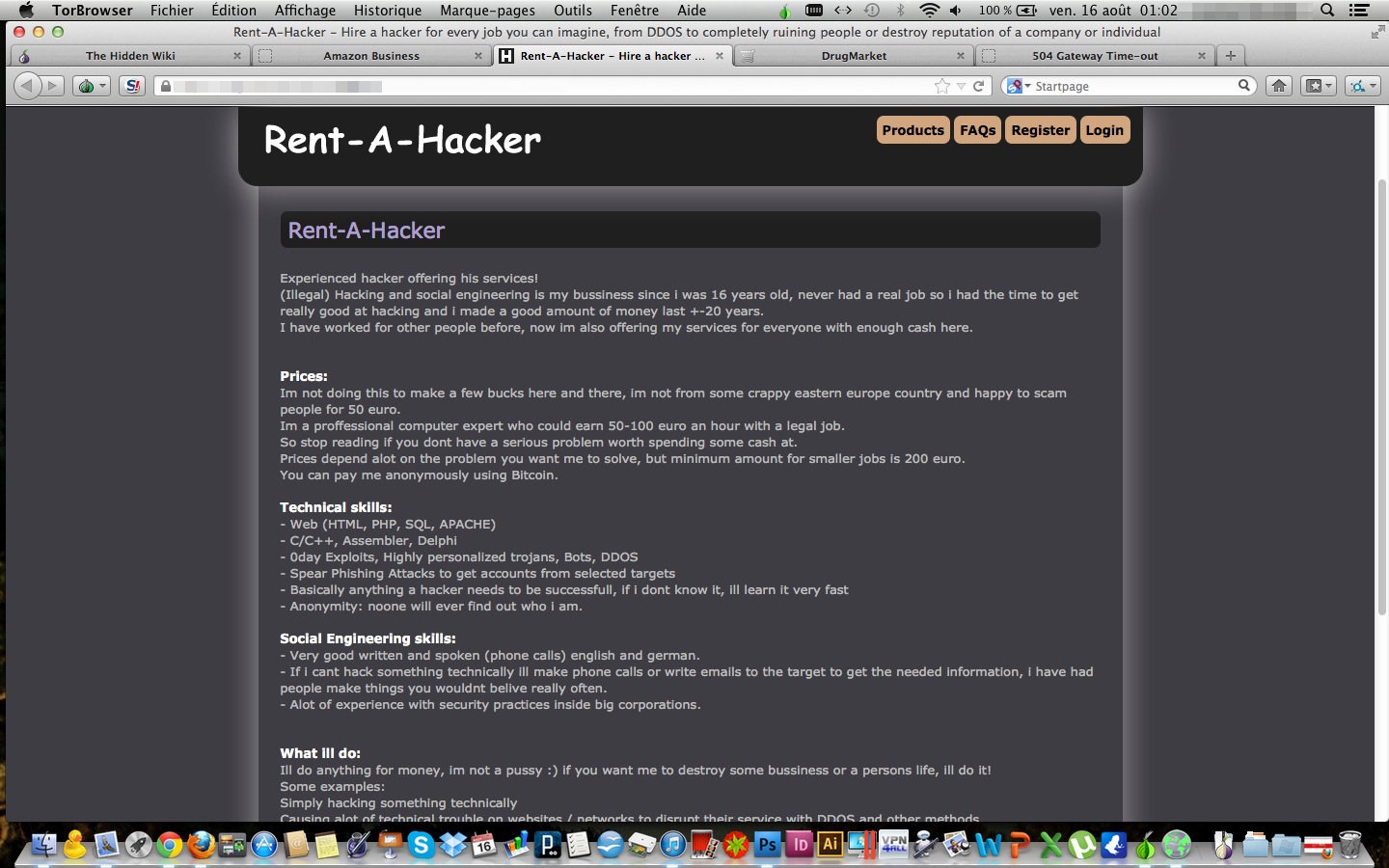
Furthermore, the legal implications of accessing dark web markets cannot be ignored. Law enforcement agencies closely track these sites, targeting illicit activities such as drug sales, weapons sales, and fraud. Individuals caught buying illegal goods can face hefty fines or even jail time, depending on the region and the seriousness of the crime. The anonymity provided by the darknet is not absolute, and various tactics, including cyber investigation, can lead to participant identification.
Moreover, there is also the risk of being exposed to harmful or malicious content. Users may inadvertently download malware or fall victim to online crimes such as hacking attempts or data breaches. Beyond monetary and legal consequences, interacting with dark web markets can compromise personal safety and privacy. The volatile nature of these environments leaves individuals exposed to threats from other users or criminal groups, making it crucial to approach the darkweb with high caution.

